Sialic Acid Raw Material Supplier
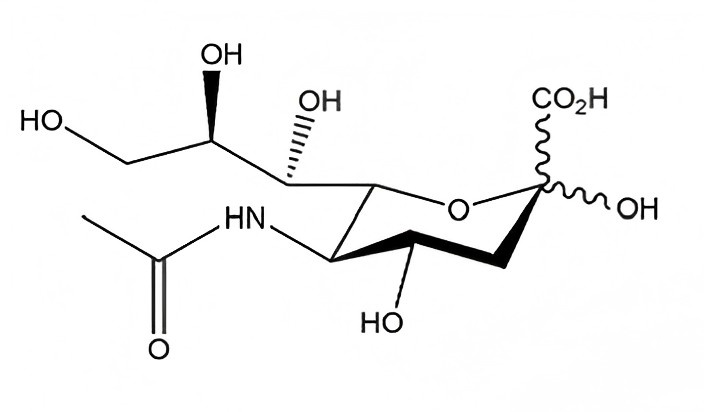
Sialic acid, also known as N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), bird’s nest acid cubilose acid,is a naturally occurring carbohydrate first isolated from brain glycolipids and salivary mucins. It belongs to a family of 9-carbon sugars, with Neu5Ac being the most abundant and biologically active form—especially valued as the key functional component in bird’s nest (cubilose), where its concentration is often used as a quality marker.
Sialic acid plays vital roles in brain development, immune regulation, cell signaling, and skin health. In the human body, it is highly concentrated in the brain, where its level is approximately 15 times that of visceral organs such as the liver or lungs.
Recent studies have also investigated its potential involvement in tumor biology, particularly in relation to immune modulation and metastasis, highlighting its value in functional and research-driven health applications.
Our sialic acid is ideal for infant nutrition, dietary supplements, functional foods, and cosmetic formulations.
Application
Promotes brain development and cognition
Sialic acid plays a very important role in the production and development of the brain and nervous system. Studies have shown that the addition of Neu5Ac in maternal mice during pregnancy improves the learning and memory functions of their offspring, suggesting the role of sialic acid in neuronal development. Infants and even the entire juvenile brain development stage need to consume enough sialic acid to ensure the normal development of brain function. After childbirth, the level of sialic acid in the mother’s body decreases over time. Therefore, consistent intake of adequate sialic acid during pregnancy and lactation can help maintain sialic acid levels in the mother’s body. There is also a clear correlation between the content of sialic acid and the content of DHA, both of which are beneficial for early brain development. Sialic acid is also helpful in adults to improve memory.
Immunity enhancing
Sialic acid has the function of antiviral and boosting the body’s immunity. Sialic acid is not degraded in the digestive system and can enter the gastrointestinal tract to bind to pathogenic microorganisms, preventing them from adsorbing to intestinal cells. The free sialic acid in the body can not only bind to the influenza virus and prevent it from binding to human cells, but also can achieve antiviral effects by inhibiting the activity of blood cytolglutinin or neuraminidase on the surface of the influenza virus.
Skin whitening
Tyrosinase is a key enzyme involved in melanin synthesis, and Neu5Ac can inhibit tyrosinase activity, thereby reducing the formation of melanin. Studies have shown that the skin whitening effects of Neu5Ac are comparable to several well-known skin whitening agents, such as hydroquinone, arbutin, and kojic acid. Arbutin is not stable enough, it is easy to oxidize, be damaged by light and decompose, and hydroquinone and kojic acid are potentially carcinogenic. The chemical structure of Neu5Ac is different from the above-mentioned whitening agents, with the phenolic ring moiety replaced by a glucose ring. Therefore, it is a safe and effective whitening ingredient.
Anti-hypertensive
Neu5Ac has vasodilatory ability and can promote the stabilization of red blood cells by preventing the aggregation of blood components. Neu5Ac is associated with lipid or cholesterol metabolism, and supplementing with Neu5Ac intake in a high-fat diet can improve lipid metabolism and hyperlipidemia-related coagulation. Therefore, sialic acid can be used as a potential supplement for antihypertensive and hyperlipidemia.
Anticancer
Sialic acid can act as a potent immunomodulator on the surface of cancer cells, providing an immunosuppressive microenvironment and tumor immune evasion. Sialic acid blocking glycomimetics enable a robust tumor immune response, enhance tumor infiltrating natural killer factor-mediated tumor cell killing, and prevent cancer metastasis.

References
Ling AJW, Chang LS, Babji AS, Latip J, Koketsu M, Lim SJ. Review of sialic acid’s biochemistry, sources, extraction and functions with special reference to edible bird’s nest. Food Chem. 2022 Jan 15;367:130755. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130755.
M.Y. Yew, R.Y. Koh, S.M. Chye, S.A. Zainal Abidin, L. Othman, K.Y. Ng. Neurotrophic properties and the de novo peptide sequencing of edible bird’s nest extracts. Food Bioscience, 32 (2019), p. 100466
Xu, Y. Shan, N. Wang, Y. Liu, M. Zhang, M. Ma. Sialic acid involves in the interaction between ovomucin and hemagglutinin and influences the antiviral activity of ovomucin International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 119 (2018), pp. 533-539
Sun, S. Zhang, J. Ren, C.C. Udenigwe. Sialic acid-based strategies for the prevention and treatment of Helicobacter pyloriinfection: Emerging trends in food industry. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 1–12 (2020)
C.-Y. Wang, L.-J. Cheng, B. Shen, Z.-L. Yuan, Y.-Q. Feng, S. Lu. Antihypertensive and antioxidant properties of sialic acid, the major component of edible bird’s nests Current Topics in Nutraceutical Research, 17 (4) (2019), pp. 376-379
Büll, T.J. Boltje, N. Balneger, S.M. Weischer, M. Wassink, J.J. Van Gemst, V.R. Bloemendal, L. Boon, J. Van Der Vlag, T. Heise, M.H. Den Brok, G.J. Adema. Sialic acid blockade suppresses tumor growth by enhancing t-cell-mediated tumor immunity. Cancer Research, 78 (13) (2018), pp. 3574-3588
Z.C.F. Wong, G.K.L. Chan, K.Q.Y. Wub, K.K.M. Poon, Y. Chen, T.T.X. Dong, K.W.K. Tsim. Completed digestion of edible bird’s nest releases free N-acetylneuraminic acid and small peptide: An efficiency method to improve functional properties. Food & Function, 9 (10) (2018), pp. 5139-5149
Zolghadri, A. Bahrami, M.T. Hassan Khan, J. Munoz-Munoz, F. Garcia-Molina, F. Garcia-Canovas, A.A. Saboury. A comprehensive review on tyrosinase inhibitors. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 34 (1) (2019), pp. 279-309
Disclaimer
The information provided on this page is for scientific and educational purposes only. Some functions described are based on preliminary research and have not been evaluated by regulatory authorities. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.