Brief introduction
Glucosamine, the hydroxyl group of glucose replaced by an amino group, is an amino monosaccharide present in the body, which is necessary for the synthesis of proteoglycans in the cartilage matrix of human joints. Glucosamine promotes cartilage synthesis, inhibits the breakdown of articular cartilage, and also has anti-inflammatory effects. It can alleviate pain symptoms in bones and joints, improve joint comfort and flexibility. It plays an important role in maintaining and improving bone health.
Glucosamine supplements on the market are mainly in the form of glucosamine sulfate, glucosamine hydrochloride and N-acetylglucosamine.
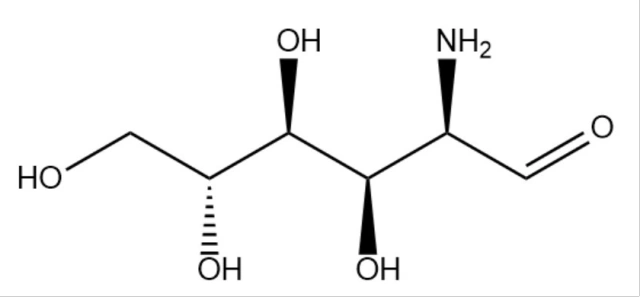
Name:Glucosamine (GlcN)
Molecular Formula :C6H13NO5
Molecular Weight:179.2
CAS No:3416-24-8
Structure:
网站.webp.png)
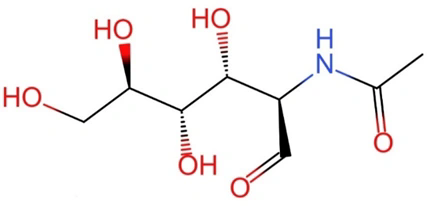
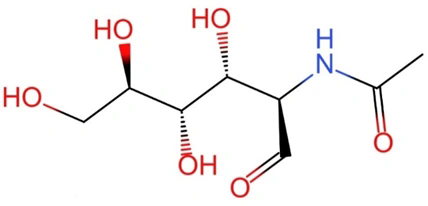
N-acetyl-D-(+)-glucosamine (GlcNAc)
Molecular Formula:C8H15NO6
Molecular Weight:221.21
CAS No:7512-17-6
Structure:
Application
Improves bone health
Glucosamine is an important nutrient for the formation of human chondrocytes and is the basic substance for the synthesis of glucoglycans. Having optimal levels of glucosamine can help support healthy bone density. The glucosamine deficiency in the human body becomes more and more severe with age, and the articular cartilage continues to degenerate and wear out. Numerous medical studies have shown that glucosamine can help repair and maintain cartilage and stimulate the growth of chondrocytes. This repair is especially important for people with osteoarthritis, whose articular cartilage is often damaged. Glucosamine promotes the repair and reconstruction of cartilage matrix by promoting the metabolic activity of chondrocytes, improving the repair ability of chondrocytes. At the same time, it also has an anti-inflammatory effect and can reduce joint discomfort in patients with osteoarthritis.
Immunity
Glucosamine participates in the metabolism of sugar in the body, and participates in the protective effect of the body by combining with other substances such as galactose, glucuronic acid and other substances to form important products with biological activity such as hyaluronic acid and keratin sulfuric acid.
Antioxidant, anti-aging
Glucosamine can increase the activity of the main antioxidant enzymes in the liver of experimental mice, and has a certain antioxidant capacity. It helps in protecting the body and cells from oxidative stress and free radicals. It is used in the manufacture of skincare and makeup products.
Mechanism of Action
Glucosamine is an important component necessary for the synthesis of proteoglycans in cartilage matrix. It synthesizes UDP-GlcNAc in vivo, which in turn synthesizes chitin, peptidoglycan, and glycosaminoglycan, and proteoglycans. UDP-GlcNAc plays an important role in protein stability, cellular structural integrity, and immune regulation. UDP-GlcNAc can be produced by the salvage nutrients glucosamine (GlcN) and N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc).
Proteoglycans can inhibit the stretching force of collagen fibers to make the articular cartilage have the function of absorbing impact force. In the later stages of joint degenerative disease, glucosaminoglycan synthesis is significantly reduced. As a result, the elasticity of the cartilage decreases and the symptoms of arthritis gradually appear. Aminomonosaccharides can stimulate chondrocytes to produce glycoproteins with normal multimeric structure, inhibit some enzymes that can damage articular cartilage (such as collagenase), prevent corticosteroids and some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from damaging chondrocytes and reduce the release of endotoxin factors from damaged cells. In the development of arthritis, supplementation with exogenous glucosamine may play a beneficial role. Glucosamine has an antioxidant effect and inhibits the production of superoxide free radicals that damage cells. The anti-inflammatory effect of glucosamine relieves the painful symptoms of osteoarthritis, improves joint function, and can stop the development of the course of osteoarthritis.

References
Rabade A, Viswanatha GL, Nandakumar K, Kishore A. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of glucosamine sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, and their combination regimen in the management of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Jun;32(3):1759-1775.
Hermann W, Lambova S, Muller-Ladner U. Current Treatment Options for Osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2018;14(2):108-116.
Vo NX, Le NNH, Chu TDP, Pham HL, Dinh KXA, Che UTT, Ngo TTT, Bui TT. Effectiveness and Safety of Glucosamine in Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. Pharmacy (Basel). 2023 Jul 14;11(4):117.
Ogata T, Ideno Y, Akai M, Seichi A, Hagino H, Iwaya T, Doi T, Yamada K, Chen AZ, Li Y, Hayashi K. Effects of glucosamine in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Sep;37(9):2479-2487.
Quik M, Hokke CH, Everts B. The role of O-GlcNAcylation in immunity against infections. Immunology. 2020 Nov;161(3):175-185.
Paneque A, Fortus H, Zheng J, Werlen G, Jacinto E. The Hexosamine Biosynthesis Pathway: Regulation and Function. Genes (Basel). 2023 Apr 18;14(4):933.
Wysoczynski M, Stephan J, Uchida S. Glucosamine regulates macrophage function in heart failure. Clin Transl Med. 2022 Apr;12(4):e819.
Bissett DL. Glucosamine: an ingredient with skin and other benefits. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2006 Dec;5(4):309-15.
Dahmer S, Schiller RM. Glucosamine. Am Fam Physician. 2008 Aug 15;78(4):471-6.
Henrotin Y, Marty M, Mobasheri A. What is the current status of chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis? Maturitas. 2014 Jul;78(3):184-7.
Nagaoka I, Tsuruta A, Yoshimura M. Chondroprotective action of glucosamine, a chitosan monomer, on the joint health of athletes. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Jul 1;132:795-800.
Anderson JW, Nicolosi RJ, Borzelleca JF. Glucosamine effects in humans: a review of effects on glucose metabolism, side effects, safety considerations and efficacy. Food Chem Toxicol. 2005 Feb;43(2):187-201.
Disclaimer
The information provided on this page is for scientific and educational purposes only. Some functions described are based on preliminary research and have not been evaluated by regulatory authorities. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.